Table of Contents
Understanding the Basics of Excel Formulas
When you think of Excel, formulas are probably one of the first things that come to mind. Formulas allow you to perform calculations, manipulate data, and automate tasks. In Excel, a formula starts with an equal sign (=) and can include a combination of numbers, operators, and cell references. But what exactly is a formula, and why are they so important in Excel?
Formulas are the backbone of Excel’s functionality, enabling users to unleash the full power of this versatile spreadsheet software. They provide a way to dynamically interact with data, enabling users to create dynamic reports, analyze trends, and make informed decisions based on the information at hand. By mastering Excel formulas, you open up a world of possibilities for data manipulation and analysis.
What is a Formula in Excel?
A formula in Excel is a mathematical expression that performs calculations on data in cells. It can include arithmetic operators such as plus (+), minus (-), multiplication (*), and division (/). Formulas can also use functions, which are predefined formulas built into Excel. These functions can perform various tasks, such as summing up values, finding averages, and counting cells that meet specific criteria.
Furthermore, Excel formulas can be as simple or as complex as needed, allowing users to create intricate calculations that cater to their specific requirements. From basic arithmetic operations to advanced statistical analysis, Excel formulas provide a robust framework for handling diverse data processing tasks efficiently and accurately.
Importance of Excel Formulas
Excel formulas are essential for data analysis and manipulation. They allow you to perform complex calculations and make sense of large datasets quickly and efficiently. By using formulas, you can automate repetitive tasks, eliminate human errors, and generate accurate results. Whether you’re working with financial data, statistical analysis, or project management, understanding and using Excel formulas will greatly enhance your productivity and effectiveness.
Moreover, Excel formulas pave the way for creating dynamic dashboards, interactive charts, and insightful visualizations that can communicate complex data trends in a clear and concise manner. With the ability to link formulas across multiple sheets and workbooks, Excel empowers users to build interconnected data models that facilitate comprehensive analysis and decision-making processes. Embracing Excel formulas is not just about performing calculations; it’s about unlocking the true potential of your data and transforming numbers into actionable insights.
Introduction to Subtraction Formula in Excel
Now that we have covered the basics of Excel formulas, let’s dive into the world of subtraction formulas. A subtraction formula in Excel allows you to subtract one number from another and get the result. This simple yet powerful formula can be used in various scenarios, such as calculating the difference between two values, determining a budget shortfall, or tracking inventory changes. Here’s everything you need to know about using subtraction formulas in Excel:
Before we delve deeper into the intricacies of subtraction formulas in Excel, it’s important to understand the fundamental concept behind this operation. Subtraction is one of the four basic arithmetic operations, alongside addition, multiplication, and division. It involves taking away a certain quantity from another to find the difference between them. In Excel, subtraction formulas follow this same principle, allowing users to perform quick and accurate calculations with ease.
Defining the Subtraction Formula
A subtraction formula consists of two or more numbers separated by the minus (-) operator. For example, to subtract the value in cell A2 from the value in cell A1, you would use the formula =A1 – A2. The result will appear in the cell where you enter the formula. You can also use cell references to subtract values from different cells, allowing for flexibility and dynamic calculations.
Furthermore, Excel provides users with the flexibility to combine subtraction formulas with other functions and operators to create more complex calculations. By nesting functions or incorporating logical operators within a subtraction formula, you can customize your analysis and derive meaningful insights from your data. This versatility makes Excel a powerful tool for financial modeling, data analysis, and decision-making processes across various industries.
When to Use the Subtraction Formula
The subtraction formula is particularly useful when you need to find the difference between two values or measure changes over time. Let’s say you have a column of sales figures for different months, and you want to calculate the monthly growth. By subtracting the previous month’s sales from the current month’s sales, you can determine the increase or decrease in revenue. This formula is also handy for calculating budgets, expenses, and analyzing financial data.
Moreover, the subtraction formula can be applied in non-financial contexts as well, such as tracking inventory levels, measuring performance metrics, or evaluating project timelines. Whether you are a business professional analyzing sales data or a student working on a math assignment, mastering subtraction formulas in Excel is essential for enhancing your computational skills and streamlining your analytical processes.
Step-by-Step Guide to Creating a Subtraction Formula in Excel
Now that you understand the concept of subtraction formulas and their applications let’s take a closer look at how to create one in Excel:
There’s no SUBTRACT function in Excel. However there are many ways to subtract numbers in Excel. Are you ready to improve your Excel skills?
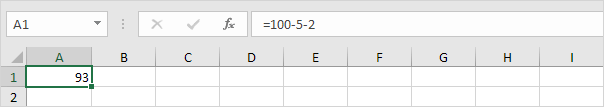
1. For example the formula below subtracts numbers in a cell. Simply use the minus sign (-) as the subtraction operator. Don’t forget always start a formula with an equal sign (=).
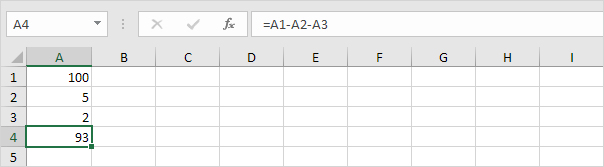
2. The formula below subtracts the value in cell A2 and the value in cell A3 from the value in cell A1.
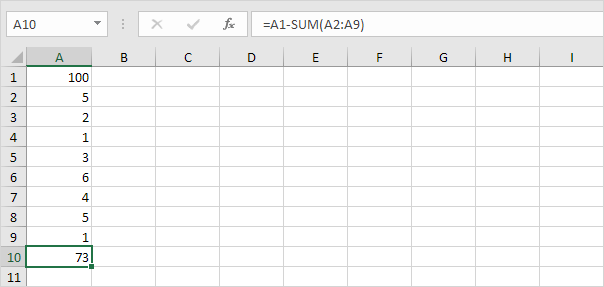
3. As you can imagine this formula can get quite long. Simply use the SUM function to shorten your formula. For example the formula below subtracts the values in the range A2:A9 from the value in cell A1.
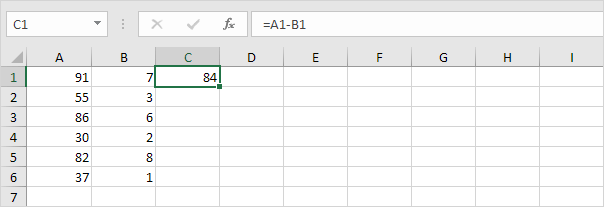
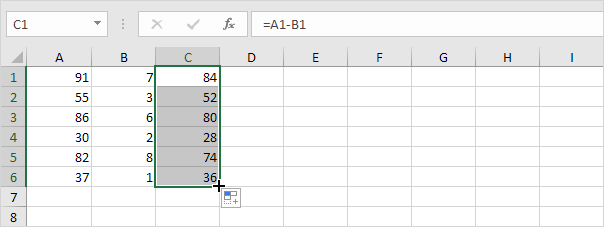
Take a look at the screenshot below. To subtract the numbers in column B from the numbers in column A execute the following steps.
4a. First subtract the value in cell B1 from the value in cell A1.
4b. Next select cell C1 click on the lower right corner of cell C1 and drag it down to cell C6.
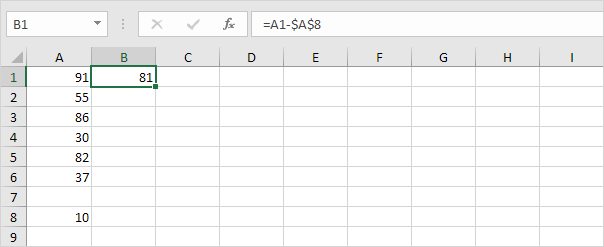
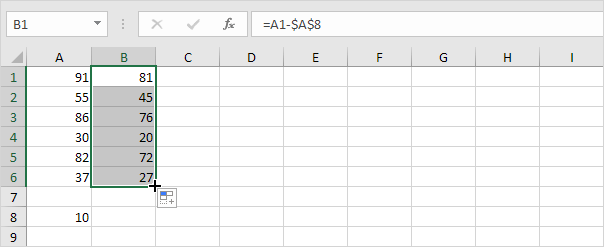
Take a look at the screenshot below. To subtract a number from a range of cells execute the following steps.
5a. First subtract the value in cell A8 from the value in cell A1. Lock the reference to cell A8 by placing a $ symbol in front of the column letter and row number ($A$8).
5b. Next select cell B1 click on the lower right corner of cell B1 and drag it down to cell B6.
Explanation: when we drag the formula down the absolute reference ($A$8) stays the same while the relative reference (A1) changes to A2 A3 A4 etc.
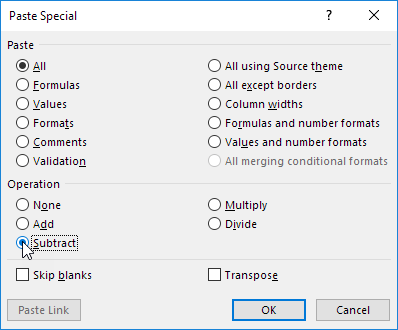
If you’re not a formula hero use Paste Special to subtract in Excel without using formulas!
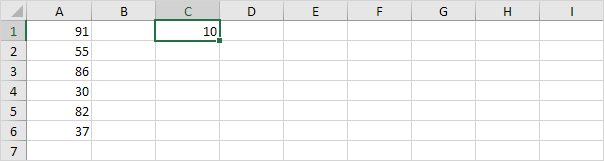
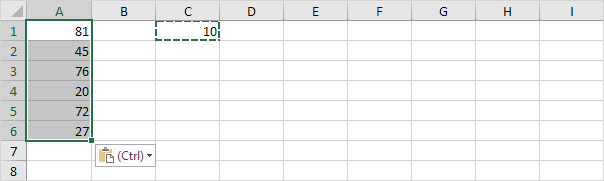
6. For example select cell C1.
7. Right click and then click Copy (or press CTRL + c).
8. Select the range A1:A6.
9. Right click and then click Paste Special.
10. Click Subtract.
11. Click OK.
Note: to subtract numbers in one column from numbers in another column at step 6 simply select a range instead of a cell.
Troubleshooting Common Errors in Subtraction Formulas
While creating subtraction formulas in Excel, you may encounter some common errors. Understanding these errors and knowing how to troubleshoot them can save you time and frustration:
Error Messages and Their Meanings
When you make a mistake in a formula, Excel displays an error message to indicate the problem. The most common error is the #VALUE! error, which occurs when the formula references cells containing text instead of numbers. Other errors include #DIV/0! for division by zero and #REF! for invalid cell references. If you encounter an error, check the formula syntax, cell references, and ensure the data types are correct.
Tips for Avoiding Formula Errors
To avoid formula errors, double-check the cell references and make sure they point to the correct cells. It’s also a good practice to use parentheses to clarify the order of operations and ensure the desired calculation. Additionally, if you’re working with complex formulas, break them down into smaller parts for easier debugging. Finally, always validate your results by comparing them with manual calculations or known values.
Advanced Subtraction Techniques in Excel
Once you have mastered the basics of subtraction formulas in Excel, you can explore advanced techniques to further enhance your calculations:
Subtracting Multiple Cells
To subtract multiple cells, you can use the SUM function. Instead of using the minus (-) operator between cell references, enclose the cell references inside the SUM function. For example, to subtract the values in cells A1, A2, and A3, the formula would be =SUM(A1,A2,A3).
Subtracting Columns and Rows
If you need to subtract an entire column or row, you can use the COLUMN and ROW functions in combination with the minus (-) operator. For example, to subtract the values in column A from column B, you would use the formula =B:B – A:A. Similarly, to subtract the values in row 1 from row 2, the formula would be =2:2 – 1:1.
With these tips and techniques, you should now have a solid understanding of how to create subtraction formulas in Excel. Whether you’re performing simple calculations or complex data analysis, Excel’s formula functionality can help you save time and improve accuracy. So go ahead and start subtracting with confidence in Excel!