Table of Contents
Running Total
This page teaches you how to create a running total (cumulative sum) in Excel. A running total changes each time new data is added to a list.
Use the SUM function
First let’s use the SUM function to create a running total in Excel.
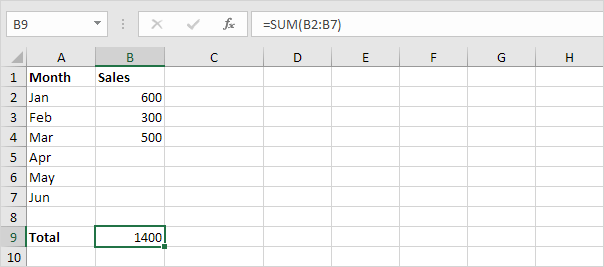
1. For example select cell B9 below and enter a simple SUM function.
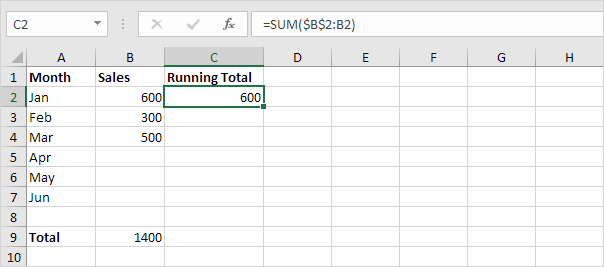
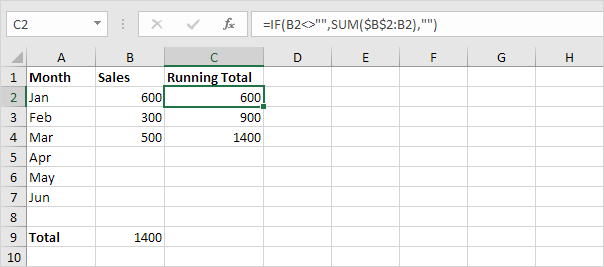
2. Next select cell C2 and enter the SUM function shown below.
Explanation: the first cell ($B$2) in the range reference is an absolute reference. We locked the reference to cell B2 by adding a $ symbol in front of the column letter and row number. The second cell (B2) in the range reference is a normal relative reference.
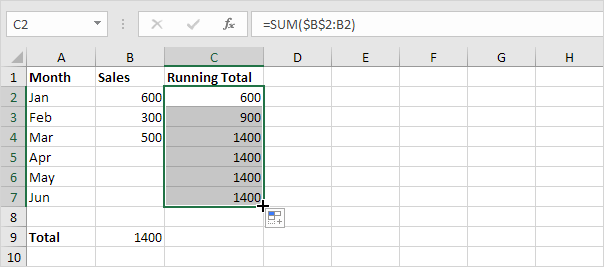
3. Select cell C2 click on the lower right corner of cell C2 and drag it down to cell C7.
Explanation: when we drag the formula down the absolute reference ($B$2) stays the same while the relative reference (B2) changes to B3 B4 B5 etc.
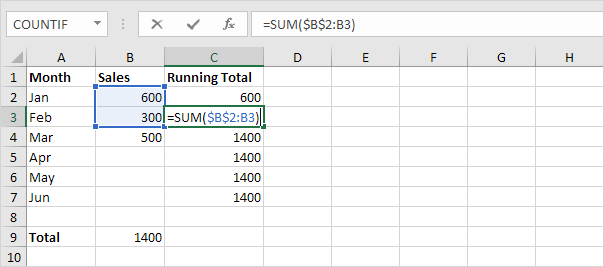
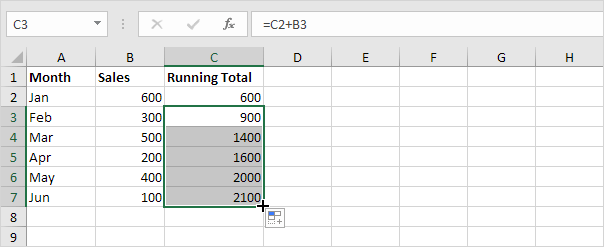
4. For example take a look at the formula in cell C3.
5. For example take a look at the formula in cell C4.
6. At step 2 add the IF function as shown below (and drag it down to cell C7) to only display a cumulative sum if data has been entered.
Explanation: if cell B2 is not empty (<> means not equal to) the IF function in cell C2 displays a cumulative sum else it displays an empty string (two double quotes with nothing in between).
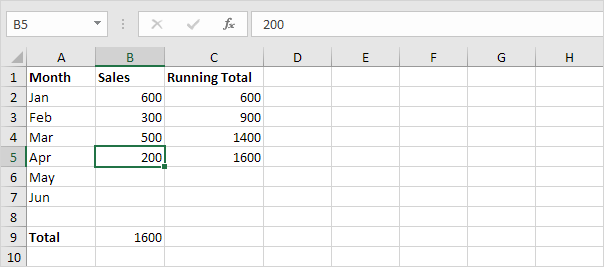
7. Enter the sales in April.
Use a Simple Formula
You can also use a simple formula to quickly calculate a running total in Excel.
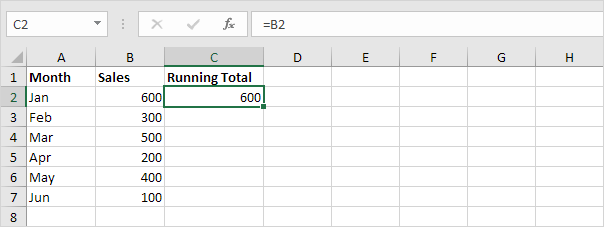
1. Start with the first value.
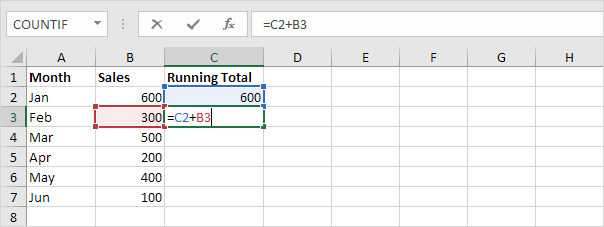
2. Add the new value to the previous running total (and copy this simple formula down).
3. Select cell C3 (not cell C2!) click on the lower right corner of cell C3 and drag it down to cell C7.
Explanation: the simple formula =C2+B3 changes to =C3+B4 =C4+B5 etc. Each time the new value is added to the previous running total.
4. You can check this.
Use the Quick Analysis Tool
Not a formula hero? No problem. You can let Excel do all the work for you!
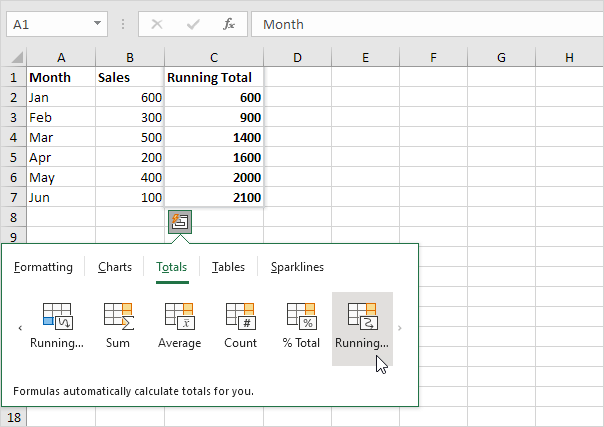
1. Select a range of cells and click the Quick Analysis button.
2. Click Totals and click Running Total (yellow-orange option).
3. The Quick Analysis tool also uses the SUM function to create a running total.
Note: now it’s your turn! Download the Excel file and try to create a running total.